In the IDA elective course "Advanced Applications: Individual Differences, Personality, and Health", students write a grant proposal on a topic to improve health in individuals with chronic diseases by promoting lifestyle change. Congratulations to Eva Schuurmans for winning (one of) the best grant proposal award!
Problem
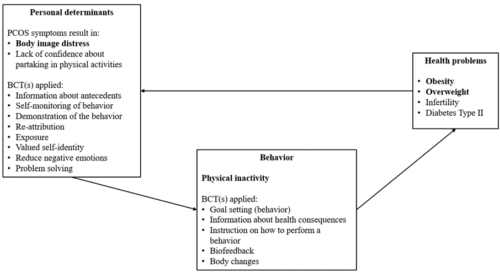
Regular physical activity is a well-established first-line strategy for both weight loss and PCOS [3, 6]. Physical activity interventions resulted in significant weight loss, reduced insulin resistance, and enhanced reproductive health features associated with the condition [7, 8]. However, many women with PCOS report difficulties maintaining a physically active lifestyle and show high attrition rates in clinical lifestyle interventions [9, 10]. Along with the aforementioned physiological health concerns, PCOS increases the risk of developing numerous psychological issues, including depression, anxiety, bulimia, anorexia, and other nonspecific eating disorders [9, 12]. Women with PCOS are also more likely to report low confidence about maintaining physical activity, the lack of safe exercise spaces, and most importantly body image distress [13–15]. These factors create substantial barriers to lifestyle management, making it more difficult for women with PCOS to engage in physical activities to improve their health outcomes. This is particularly concerning as physical inactivity contributes to weight gain, in turn enhancing body image distress [9]. The connection between physiological and psychological health underscores the complexity of managing PCOS symptoms and highlights the need for integrated interventions addressing both aspects. However, no studies have targeted both body image distress and physical activity to break this cycle (see Figure 1).
Figure 1
Envisioned Solution
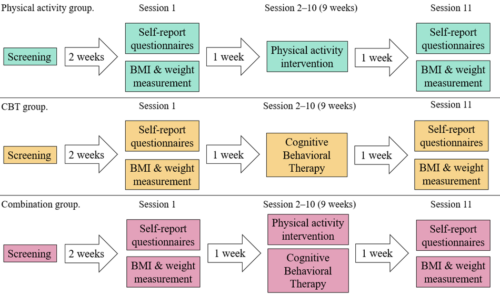
The envisioned solution is the development of a multidisciplinary lifestyle intervention for overweight and obese women with PCOS. The primary goal of the Physical Activity Body Image project (PABI-project) is to make it easier for women with PCOS to adhere to a physically active lifestyle by reducing the barrier that body image distress creates. This personalized intervention is comprised of a physical activity intervention aimed at learning how to increase physical activity levels while improving body image through cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). The effectiveness of the intervention will be tested through a randomized control trial (RCT). Participants will be randomly assigned to one of the three intervention groups: 1) the physical activity group, 2) the CBT group, or 3) the combination group (receiving both the physical activity intervention and CBT). Therefore, our study seeks to find an answer to the following research question: Will a personalized physical activity and cognitive behavioral therapy intervention significantly reduce BMI and body image distress in overweight or obese women with PCOS, compared to the control groups?
This grant proposal aligns with the HSRI cross-cutting theme ‘Personalized Interventions and Care’ by creating an intervention specifically tailored to PCOS-related problems in adhering to a physically active lifestyle. Through the integration of CBT to address body image distress, this proposal suggests a multidisciplinary approach to lifestyle interventions with the goal of helping these women adhere to a physically active lifestyle.






Be First to Comment